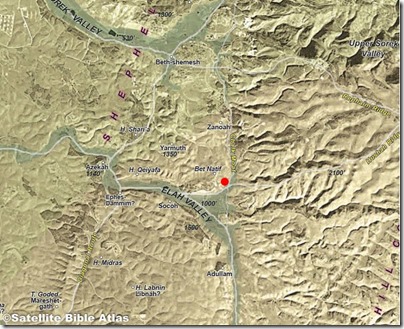
The road is located near the junction of the “Chalk Moat” route running south from Beth Shemesh and the Elah Valley road that runs up into the Judean Hill Country towards Bethlehem and Jerusalem.
On a modern map, the road is near the intersection of Highways 375 and 3855.
The Israel Antiquities Authority has determined that the road is about 20 feet (6 m) wide and one mile (1.6 km) long, but only 150 meters of the road have been exposed and will be preserved for visitors to view.
The ancient road was a spur that apparently connected the ruin of Khirbet Beit Natif on the hills north of the Elah Valley with the “Emperor’s Road.” This latter road was constructed in the time of Hadrian and ran from Bet Guvrin (ancient Eleutheropolis) through the Elah Valley near the newly discovered road and then up into the hills along the Hushah ridge.
Ilan Ben Zion identifies Beit Natif as the first-century site of Bethletepha, “a town sacked by
Vespasian’s army during the First Jewish Revolt, between 66 and 70 CE.”
Coins were discovered between the pavement stones that suggest a first-century date:
- a coin of Pontius Pilate, dating to AD 29
- a coin of Agrippa I, dating to AD 41 and minted in Jerusalem
- a coin from Year 2 of the Jewish Revolt (AD 67)
All photos in this post were taken earlier today by Bill Schlegel. More photos from the IAA are posted here.
It’s too bad that when they laid a similar water pipeline along the Roman road to Emmaus from Jerusalem that they didn’t take steps to preserve it.
HT: Joseph Lauer, David Bivin