(Post by Seth M. Rodriquez)
In our everyday lives, most of us feel far removed from the biblical world. The stories of Israelites and Judeans, Assyrians and Babylonians, and Jews and Romans seem like they happened long ago in a far off place. And yet every now and then you run across something that makes you think about how connected we are with those times. Our picture of the week is one such example.
We continue our series on obscure sites in the Pictorial Library of Bible Lands with a photograph of some of the inscriptions at Nahr el-Kalb (a.k.a., Dog River) in Lebanon. There is a limestone cliff near the end of the river, and the inscriptions carved on that cliff are a virtual “Who’s Who” of military leaders who have passed through the area in both ancient and modern times. In the map below, you can see the site’s location along the coast of Lebanon between Byblos and Beirut. (Thanks again are due to A.D. Riddle for the map graphic.)
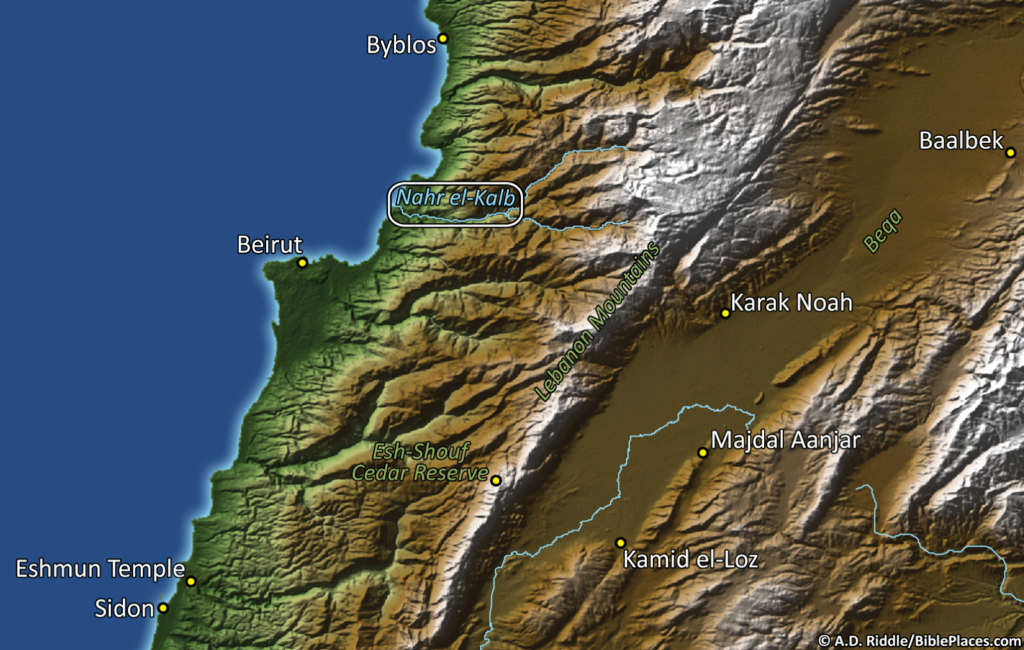
There are numerous inscriptions on this cliff, ranging from 1276 BC to AD 2000. These inscriptions commemorate the actions of Ramses II (Egyptian pharaoh in 13th c. BC), Esarhaddon (Assyrian king in 6th c. BC), Caracalla (Roman emperor in 3rd c. AD), Proculus (Phoenician governor in 4th c. AD), Barquq (Mamluq sultan in 14th c. AD), Napoleon III (French emperor in 19th c. AD [not to be confused with his uncle, Napoleon Bonaparte]), and others. Not all of the inscriptions are about military victories. Some of them just commemorate road improvements or the construction of a bridge. Yet the fact that leaders from various times and places all carved inscriptions in this place over the course of over 3,000 years is quite remarkable. This site provides us with a visible link between the modern day and all of the historical periods from the time of the ancient Egyptians onward.
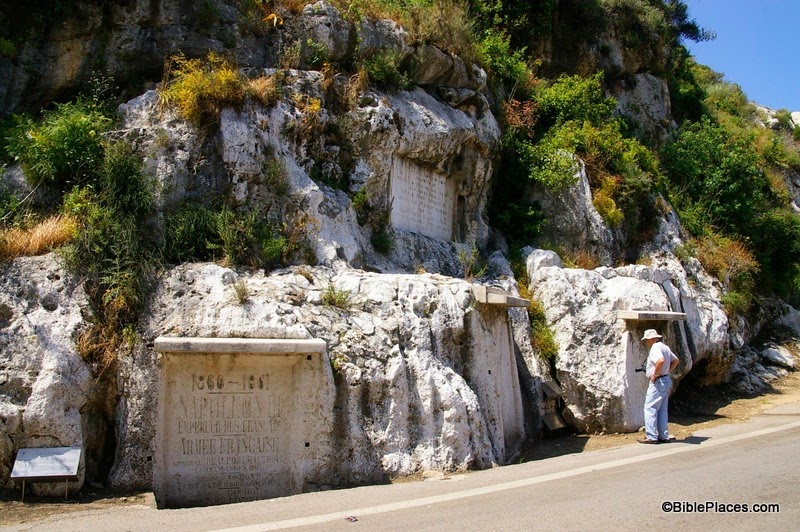

For example, in the photograph above (taken by A.D. Riddle) you can see four inscriptions clustered together (click on the photo to enlarge). The one on the left was originally an Egyptian stela carved by the army of Ramses II in the 13th century BC. In AD 1861, this space was re-used by Napoleon III to commemorate the French intervention in the war between the Druze and Maronites. The two inscriptions to the right of Napoleon’s were carved by the ancient Assyrians (the man in the picture is looking at one and the other can be seen directly behind him). The texts of these two stelae have not endured the ravages of time, but the relief of an Assyrian king can still be seen on one of them. These inscriptions date to sometime in the Iron Age. Above the Assyrian stelea, you can see an inscription carved by the British Desert Mountain Corps during World War I, which records their military victories at Damascus, Homs, and Aleppo in 1918.
So in this one photograph we have the armies of ancient and modern nations represented. The juxtaposition of ancient Egypt and Assyria with the French and British reminds us that we are all part of an unbroken string of history. We are not so far removed from the ancients as we think.
This photograph and map, along with over 700 other images, are included in Volume 8 of the Pictorial Library of Bible Lands, and is available here for $34 (with free shipping). Further images of the inscriptions at Nahr el-Kalb can be found here at LifeintheHolyLand.com, and photographs from nearby Byblos can be seen here on BiblePlaces.com.